Cell Thawing Experiment
A cell thawer is a laboratory device used for the rapid and safe thawing of cryopreserved cell samples. It is widely applied in fields such as cell culture and biopharmaceuticals. Its core function lies in precise temperature control and programmed operation, which help to maximize cell viability during the thawing process while avoiding contamination or temperature fluctuation-related damage that may occur with traditional water bath methods.
Target:
Cell samples thawed using the cell thawer and those thawed using the traditional water bath method were tested with a fluorescence cell counter to verify that the cell thawer can maintain cell viability and reduce cell damage during the thawing process.

Experimental scheme:
1、Take out CHO cells, HEK293 cells, and MSC cells from the liquid nitrogen tank;
2、Cells were thawed using the Eyecute cell thawer (labeled as Cell1-C, Cell1-H, and Cell1-M), and cells were thawed using a water bath (labeled as Cell2-C, Cell2-H, and Cell2-M);
3、The viability of Cell1-C, Cell1-H, Cell1-M, Cell2-C, Cell2-H, and Cell2-M was respectively tested using the Tuger fully automated multi-channel fluorescence cell analyzer.
Result:
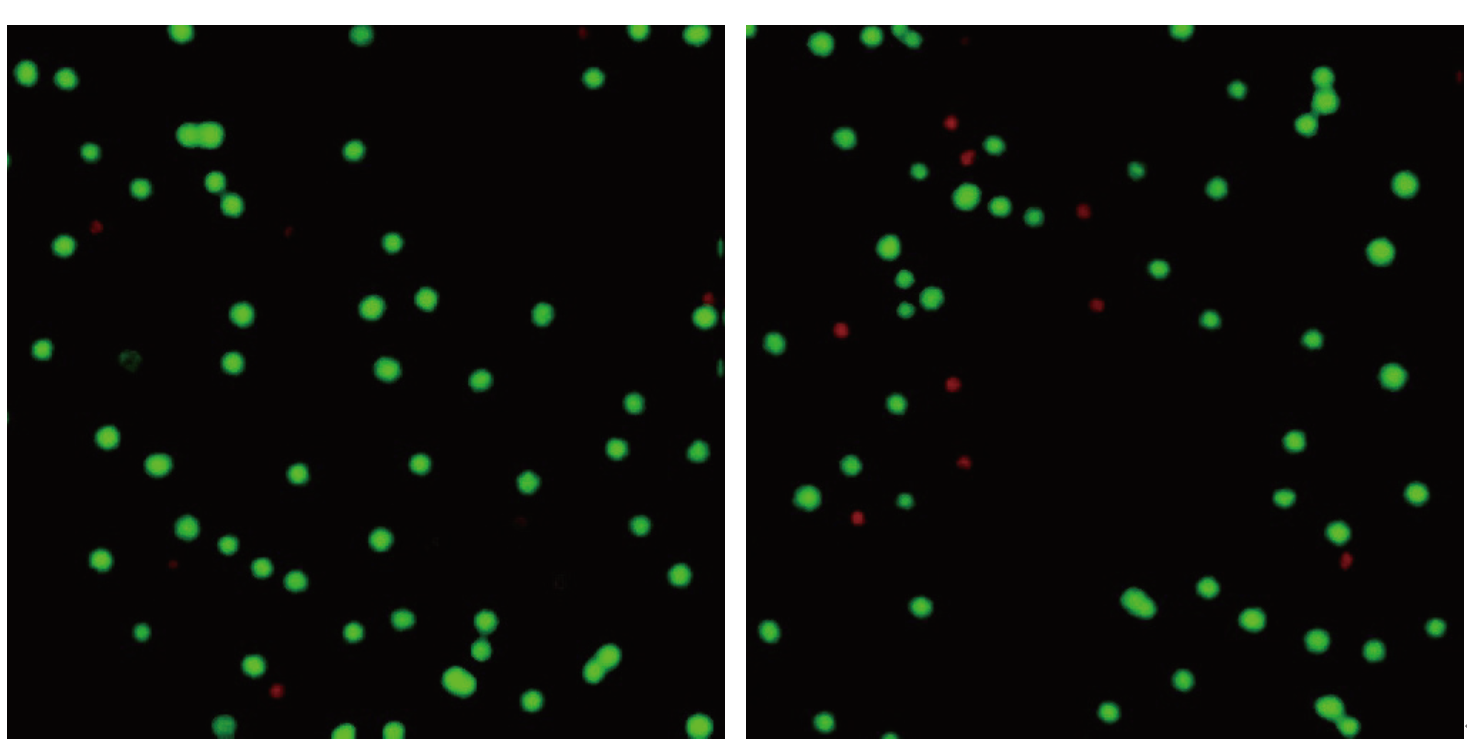
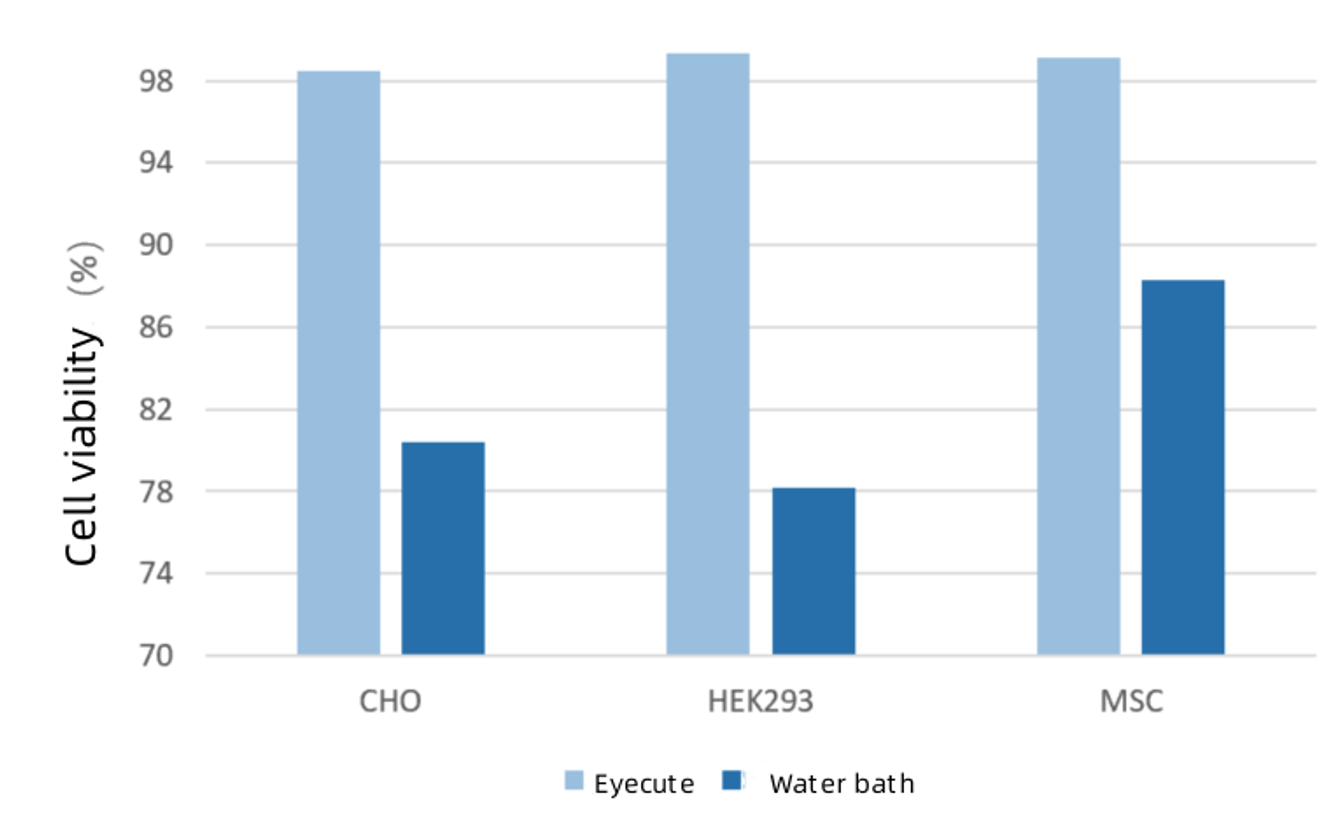
Comparison of cell viability between the cell thawer and water bath
Conclusion:
Cells thawed using the Eyecute cell thawer exhibited viability rates above 98%, while cells thawed using the water bath showed viability rates ranging from 75% to 90%. The cell thawer achieves higher cell viability, effectively prevents various types of biological contamination, saves thawing time, and improves experimental efficiency.

National Advisory Service Hotline
Sales consultation: +86 15322248165(Whatsapp/Wechat)
E-mail:global@newtonoptic.com
R & D Center: Room 301, Floor 1, Building 1, No.38 Gaopu Road, Tianhe District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province

Follow Wechat Official Account
©2024 Guangzhou Newtonoptic Research Institute Co., Ltd. All rights reserved